Forex and CBDC: Exploring the Empowering Partnership
- June 9, 2021
- Jennifer Moore

The instant payment facility of the CBDC as opposed to the existing model of the payment transaction in central bank money would serve to greatly reduce settlement risks. Therefore, the Forex market is the largest financial market and would most likely rank among the largest beneficiaries of central bank digital currency. Therefore, the instant payment facility of the CBDC as opposed to the existing model of the payment transaction in central bank money would serve to greatly reduce settlement risks. Thereafter, this should also create new business models to supplant the prevalent arrangement for trading and settlement.
Therefore, it could propagate a more effective distribution of central bank liquidity including in international settings, and reduce financial risk globally. Moreover, the use of CBDC may bring down annual expenses related to forex by $130 billion.
Also Read: Life of forex market in the upcoming years
The Troubles Faced By Forex
The forex constitutes the largest financial market and is the main user of central bank money. However, the foreign exchange currently faces a list of issues that need to be addressed.
1. It endures a long time-lapse between trading and settlement.
2. Moreover, it lacks transparency.
3. It entails surmounting high risks.
The Risks and Settlement Methods of the Forex Market
The main risk in foreign exchange trading is the settlement risk. Therefore, Settlement risks eclipse the credit risk and liquidity risk.
Credit risk happens when counterparties fail to deliver the currency or default on a Vostro account claim when subject to an insolvency procedure.
Liquidity risk arises when the counterparties do not settle the full value in time. Therefore, disabling the payee’s capacity to meet their own requirements. Thus, demanding an alternative resource to mobilize funds for immediate commitment at short notice. Therefore, this also reduces the ability to reuse committed funds.
Enter CBDC
CBDC represents a format of central bank money that is fully fungible with other central bank monetary liabilities. Thereafter, the token format takes on properties aimed at facilitating versatile access methods to additional functionalities for central bank money.
Moreover, the tokens are programmable. Therefore, this allows them to root- in the much-needed prudential and other monetary policy and financial stability parameters to protect and discipline CBDC circulation. Moreover, CBDC is also viewed as a substrate for further financial innovation with extended support features for the token-based financial ecosystems. Therefore, this also encompasses settlement in the token-based financial market infrastructures. Furthermore, it propels greater diversification in payments.
The issuance and trading of CBDC are best attained using a permissioned distributed ledger technology (DLT)-enabled network to ensure optimum performance, security, transferability, and privacy in transactions. The issuance of CBDC would be solely under the guardianship of the central bank. However, the network is to be maintained by the central bank and a number of resident financial institutions serving as operators of network nodes that validate and record all transactions. The tokens are to be controlled by private keys stored in electronic wallets. The electronic wallets could be held outright or via a custodial relationship included by resident banks of the issuing currency country.
Instant and Atomic Settlements
The adoption of tokens sanctions the simultaneous execution of trading and settlement in one transaction; enabling instant and atomic settlement through simple exchanges of tokens (atomic swaps). The programmability of tokens assure that transactions are instant and are committed only upon meeting certain conditions.
The atomic swaps would enforce the risk mitigation measures and preclude any deferment between trading and settlement. This ensures both currency legs are available at the same time and allow for real-time reuse. Liquidity management would be eased as trading positions would not impede liquidity against the immediate availability of funds.
Use Cases of CBDC and Forex-Related Trading
The use cases depicting the relationship of the two important financial instruments are illustrated below.
The entities participating in the possible transactions include:
1. The domestic central bank issuing a domestic CBDC
2. Foreign central banks issuing a foreign CBDC
3. Domestic commercial banks (DBS), including a domestic commercial bank issuing a tokenized security
4. Foreign commercial banks (FBs)
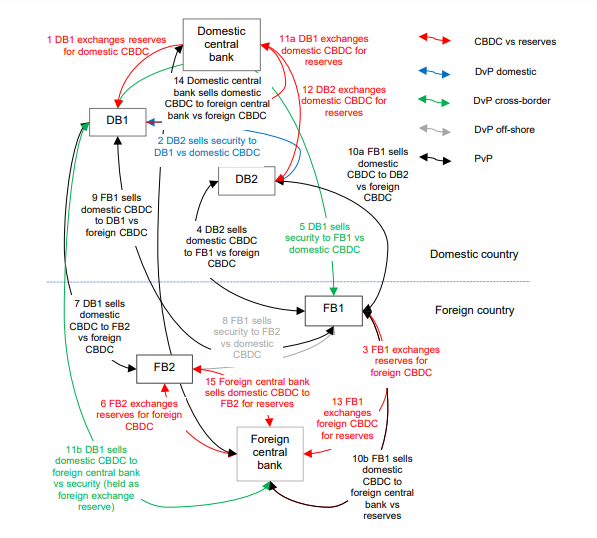
The possible transactions include (Figure):
1. DB1 exchanges reserves for a domestic CBDC at the domestic central bank.
2. DB2 sells a security to DB1 against domestic CBDC in an instant and atomic DvP transaction
3. FB1 exchanges reserves for a foreign currency CBDC at a foreign central bank
4. DB2 sells domestic CBDC to DB1 against a foreign currency CBDC in an instant and atomic PvP cross-border transaction
5. DB1 sells a security to FB1 against domestic CBDC in an instant and atomic DvP cross-border transaction
6. FB2 exchanges reserves for a foreign currency CBDC at a foreign central bank
7. DB1 sells domestic CBDC to FB2 against foreign currency CBDC in an instant and atomic PvP cross-border transaction
8. FB1 sells a security to FB2 against domestic CBDC in an instant and atomic DvP off-shore transaction
9. FB1 sells domestic CBDC to DB1 against foreign currency CBDC in an instant and atomic PvP cross-border transaction
10. (A) FB1 sells domestic CBDC to DB2 against foreign currency CBDC in an instant and atomic PvP cross-border transaction
(B) Moreover, FB1 sells domestic CBDC to foreign central bank against reserves
11. (A) DB1 exchanges domestic CBDC for reserves at the domestic central bank
(B) DB1 sells domestic CBDC to the foreign central banks in an instant and atomic DvP cross-border transaction.
12. DB2 exchanges domestic CBDC for reserves at the domestic central bank
13. FB1 exchanges foreign currency CBDC for reserves at a foreign central bank
Also Read: Crypto opportunities for forex derivatives brokers
14. Moreover, the domestic central bank sells domestic CBDC to foreign central bank against foreign CBDC in an instant and atomic PvP cross-border transaction
15. Thereafter, the foreign central bank sells domestic CBDC to FB2 against reserves
Figure. Possible CBDC and securities life cycles
Support Functions
Furthermore, CBDC Forex support functions touch upon the following
1. Foreign Exchange Spot trading
2. Foreign Exchange Swap trading
3. Collateralization
4. CBDC as foreign exchange reserves
5. Federal Reserve dollar liquidity swap lines
6. International settlement of securities
To Conclude
The DLT-enabled networks seek to provide the much-needed features options, and security to control access, trading, and settlement. Moreover, the marked separation of network operators and wallet holders enables a two-tiered approach in foreign exchange trading. Therefore, this allows seamless transactions between resident and non-resident entities. Thereafter, while maintaining operational autonomy with resident entities. Moreover, it seeks to protect existing regulatory and supervisory reign while extending its reach.
Categories
- AI (6)
- Altcoins (10)
- Banking (10)
- Bitcoin (132)
- Bitcoin ETF (11)
- Bitcoin Price (30)
- Blockchain (47)
- Brokering World Hunger Away (16)
- Business (7)
- CBDC (11)
- COVID-19 (3)
- Crypto ATMs (1)
- Crypto Banking (15)
- Crypto Bill (1)
- Crypto broker platform (26)
- Crypto Investment (3)
- Crypto Markets (3)
- Crypto Payment (26)
- Crypto Prices (1)
- Crypto Trading (88)
- Cryptocurrency (365)
- Cryptocurrency Exchange (95)
- Data Visualization (2)
- Decentralized Finance (7)
- DeFi Payment (9)
- DEX (3)
- Digital Currency (22)
- Ethereum (2)
- FAQ (6)
- Finance (24)
- Financial Equality (4)
- Financial Freedom (8)
- Forex (24)
- ICO (1)
- Investment (11)
- Mining (3)
- News (64)
- NFTs (2)
- P2P (1)
- PayBitoPro (606)
- PayBitoPro Coin Listing (6)
- PayBitoPro Exchange (2)
- Post COVID Digital Transformation (1)
- Press Release (130)
- Privacy & Security (3)
- Real Estate (1)
- Stablecoin (4)
- Technology (14)
- Uncategorized (2)
- US Presidential Election (2)
- Utility Coin (1)
- Web3 Wallets (1)
- White Label Crypto Broker Solution (1)
- White Label Crypto Exchange (6)